Polymeric complex micelles based on the double-hydrazone linkage and dual drug-loading strategy for pH-sensitive docetaxel delivery
Abstract
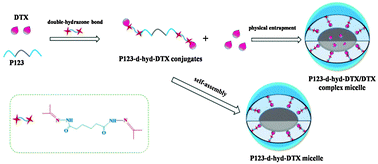
Stimuli-triggered drug release and improved drug loading are two key prerequisites in the preparation of nano-drug delivery systems. Herein, we constructed the first pluronic P123-double (d)–hydrazone bond (hyd)–docetaxel (DTX)/DTX complex micelles (P123-d–hyd–DTX/DTX) which integrated the highly pH-sensitive strategy and the dual drug-loading pattern in one platform. We synthesized pluronic P123-double (d)–hydrazone bond (hyd)–docetaxel (DTX) conjugates (P123-d–hyd–DTX) by conjugating DTX to the PEO chains of P123 via two hydrazone linkages in the backbone for the first time. An increase in the number of hydrazone linkages within the unimolecular conjugate was conducive to improve the pH sensitivity of conjugated-based micelles. Besides, aiming at improving drug loading, the dual drug-loading strategy (chemical conjugation and physical encapsulation) was adopted. Namely, pH-sensitive P123-d–hyd–DTX was used as a vehicle to further encapsulate DTX for preparing P123-d–hyd–DTX/DTX complex micelles. The resulting P123-d–hyd–DTX/DTX micelles exhibited intact spherical shape, uniform particle size distribution (110.37 nm) and higher drug loading (12.64%). The release study in vitro confirmed that P123-d–hyd–DTX/DTX micelles and P123-d–hyd–DTX micelles (as a control) showed highly pH-responsive release properties. In particular at pH 6.5, almost 90.9% and 75% of DTX was released within 48 h, respectively. Compared to P123-d–hyd–DTX micelles, P123-d–hyd–DTX/DTX complex micelles exhibited higher proliferation inhibition effects on B16F10 cells (p < 0.01), while the cytotoxicity of P123-d–hyd–DTX/DTX complex micelles was slightly inferior to that of free DTX (p < 0.05). In the xenograft B16F10 melanoma model, P123-d–hyd–DTX/DTX complex micelles suppressed tumor growth more effectively than Duopafei® (p < 0.01) and P123-d–hyd–DTX micelles (p < 0.05), without causing obvious adverse effects. Overall, the novel polymeric complex micelle based on double-hydrazone bond and dual drug-loading strategies was a promising delivery platform to improve therapeutic efficiency and decrease side effects in cancer treatments.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...