Novel biocompatible electrospun gelatin fiber mats with antibiotic drug delivery properties†
Abstract
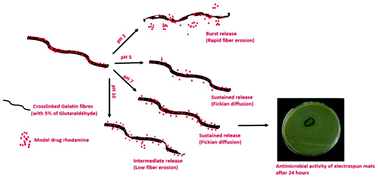
The aim of this study was to synthesize stable gelatin electrospun mats (ESMs) (cross-linked by glutaraldehyde (GTA) vapors) with tunable drug release properties using pH as a stimulus. Gelatin ESMs loaded with rhodamine as a model drug were first synthesized. The in vitro release of rhodamine was characterized to understand the mechanisms of drug release and the effects of both cross-linker concentration and pH on drug release. An optimal cross-linker concentration of 5% was evidenced to provide ESMs allowing both sustainable release of drugs at pH 7 and burst release at pH 2. The release profiles were then fitted with a power law model to describe the release kinetics. The chlorhexidine antibiotic drug was finally loaded into the optimal electrospun mat and its bactericidal activity was demonstrated against Gram-negative (E. coli) and Gram-positive (S. epidermidis) bacteria by agar diffusion tests. This biocompatible material was shown to efficiently destroy bacterial biofilms and prevent bacterial growth within a short time (3 h), while maintaining its antibacterial activity up to at least 72 h. This study provides a promising material, which could treat infected sites and prevent infections, with tunable drug releasing properties using pH as a stimulus.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...