Pluripotency maintenance of amniotic fluid-derived stem cells cultured on biomaterials
Abstract
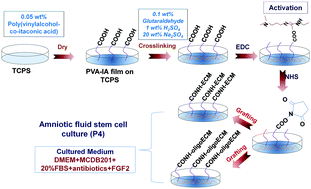
The stem cell fates of pluripotency and differentiation are regulated by not only soluble biological cues but also insoluble biochemical cues (i.e., extracellular matrix (ECM)) and the physical cues of cell culture biomaterials (i.e., elasticity). We investigated the maintenance of pluripotency and the differentiation lineages of human amniotic fluid-derived stem cells (hAFSCs) cultured on poly(vinyl alcohol-co-itaconic acid) (PVA) hydrogels grafted with several types of ECM and corresponding oligopeptides in expansion medium. hAFSCs cultured on soft PVA hydrogels (12.2 kPa) that were grafted with oligopeptides derived from fibronectin and vitronectin showed high pluripotency, which was evaluated by Oct4, Sox2 and Nanog expression. The hAFSCs grown on soft PVA hydrogels (12.2 kPa) grafted with each oligopeptide showed higher pluripotency, as assessed by Oct4 and Nanog expression, than hAFSCs grown on stiff PVA hydrogels (25.3 kPa) grafted with the same oligopeptides and a much higher pluripotency than those grown on rigid tissue-culture polystyrene dishes. Soft biomaterials appeared to be adequate to maintain the pluripotency of hAFSCs. Surprisingly, hAFSCs that showed higher pluripotency on PVA hydrogels grafted with oligopeptides derived from fibronectin and vitronectin also expressed higher levels of early differentiation markers for three germ layers in expansion medium. This result suggests that hAFSCs are heterogeneous and that this population contains highly pluripotent stem cells and stem cells that can be easily differentiated.
 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...