Phenylboronic acid-modified magnetic nanoparticles as a platform for carbon dot conjugation and doxorubicin delivery†
Abstract
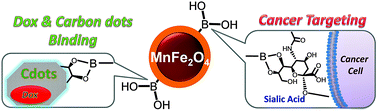
We describe the preparation of phenylboronic acid-modified magnetofluorescent nanoparticles (NPs) consisting of MnFe2O4 magnetic NPs conjugated to fluorescent carbon dots (Cdots). These NPs are useful for both optical and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) modalities and could also be used to deliver the water-insoluble chemotherapy drug, doxorubicin (Dox). In this study, hydrophobic MnFe2O4 NPs were transferred from organic media to water by coordinating with 4-carboxyphenylboronic acid ligands, which also act as a cancer cell-specific targeting ligand and a site for conjugation to fluorescent Cdots, allowing the preparation of phenylboronic acid-modified magnetofluorescent NPs. The NPs displayed colloidal stability at different pH values and salt concentrations, and exhibited negligible cytotoxicity against HeLa cancer cells with >85% cell viability at concentrations of up to 500 μg mL−1. Confocal laser scanning microscopy showed the specificity of the magnetofluorescent NPs in HeLa cells. MRI experiments showed that the magnetofluorescent NPs were effective contrast enhancement agents in T2-weighted MRI. Moreover, the NPs were also found to be effective fluorescent markers in an in vivo experiment in zebrafish embryos. Dox was attached to the NPs by π–π stacking interactions, and was delivered in a targeted manner. The results indicated that these magnetofluorescent NPs could deliver Dox efficiently and induce an anticancer effect in HeLa cells, as confirmed by confocal laser scanning microscopy and in vitro cytotoxicity assays.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...