Construction of d-α-tocopheryl polyethylene glycol succinate/PEO core–shell nanofibers on a blood-contacting surface to reduce the hemolysis of preserved erythrocytes†
Abstract
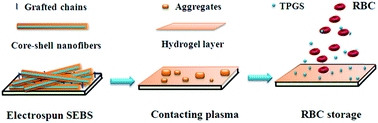
The hemolysis of erythrocytes is a big obstacle to the development of new non-plasticizer polymer containers for erythrocyte preservation. To construct a long-term anti-hemolytic surface of a plasticizer-free polymer, we coaxially electrospin core–shell structured D-α-tocopheryl polyethylene glycol 1000 succinate (TPGS)/poly(ethylene oxide) nanofibers on the surface of a styrene-b-(ethylene-co-butylene)-b-styrene (SEBS) elastomer that is covered with grafted poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) chains. Our strategy is based on the fact that the grafted layers of PEG reduce mechanical damage to red blood cells (RBCs) while the TPGS released from the nanofibers on a blood-contacting surface can act as an antioxidant to protect RBCs from oxidative damage. We demonstrate that TPGS/PEO core–shell structured nanofibers have been well prepared on the surface of PEG modified SEBS; the controlled release of TPGS in distilled water is obtained and the release can last for almost 4 days at 4 °C; during RBC preservation, TPGS acts as the antioxidant to decrease the membrane oxidation and hemolysis of RBCs. Our work paves a new way for the development of non-plasticizer polymers for RBC preservation, which may be helpful for the fabrication of long-term anti-hemolytic biomaterials in vivo.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...