A novel pseudo-protein-based biodegradable coating for magnesium substrates: in vitro corrosion phenomena and cytocompatibility
Abstract
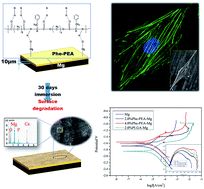
The goal of this study is to examine whether a member of the newly developed biodegradable pseudo-protein biomaterial family could provide a far better protection and performance than the popular hydrolytically degradable poly(glycolide-co-lactide) (PLGA) biomaterial on an experimental magnesium substrate as a model. A member of the phenylalanine-based poly(ester amide)s, (8-Phe-4), was chosen as a model pseudo-protein polymer to coat onto as-cast magnesium (Mg) metal as the experimental model. The microstructures of the coatings were characterized by SEM, FTIR and water contact angle measurements. Nano-scratch test data indicated that the scratch resistance and elastic resilience of the 8-Phe-4 coating were superior to the PLGA coating. Standard electrochemical measurements along with the long-term immersion results indicated that the 8-Phe-4-coated Mg had preferable in vitro degradation and corrosion behavior than the PLGA-coated Mg. The cytocompatibility test was conducted via vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) and human umbilical vein endothelial cells (ECV304), and the 8-Phe-4-coated Mg showed significantly better cell viability than the pure Mg and PLGA-coated Mg substrates over a 3 day incubation period. The favorable anti-corrosion behavior and cytocompatibility of the 8-Phe-4 coating suggest that the newly developed biodegradable pseudo-protein biomaterials may have great potential as biodegradable coating materials to enhance the protection and performance of Mg-based biomaterials and their application compared to the popular PLGA, and may bring the application of Mg-based biomaterials closer to clinical reality.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...