A biocompatible and functional adhesive amine-rich coating based on dopamine polymerization†
Abstract
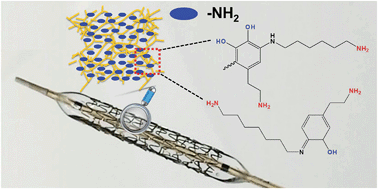
Amine groups physiologically play an important role in regulating the growth behavior of cells and they have technological advantages for the conjugation of biomolecules. In this work, we present a method to deposit a copolymerized coating of dopamine and hexamethylendiamine (HD) (PDAM/HD) rich in amine groups onto a target substrate. This method only consists of a simple dip-coating step of the substrate in an aqueous solution consisting of dopamine and HD. Using the technique of PDAM/HD coating, a high density of amine groups of about 30 nmol cm−2 was obtained on the target substrate surface. The PDAM/HD coating showed a high cross-linking degree that is robust enough to resist hydrolysis and swelling. As a vascular stent coating, the PDAM/HD presented good adhesion strength to the substrate and resistance to the deformation behavior of compression and expansion of a stent. Meanwhile, the PDAM/HD coating exhibited good biocompatibility and attenuated the tissue response compared with 316L stainless steel (SS). The primary amine groups of the PDAM/HD coating could be used to effectively immobilize biomolecules containing carboxylic groups such as heparin. These data suggested the promising potential of this PDAM/HD coating for application in the surface modification of biomedical devices.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...