Porous fluorine-doped tin oxide as a promising substrate for electrochemical biosensors—demonstration in hydrogen peroxide sensing†
Abstract
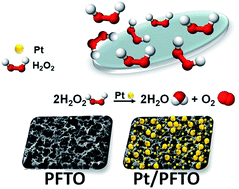
Conducting porous substrates of high hydrophilicity are advantageous in applications of electrochemical biosensors as host electrodes, offering not only fast charge transport and large sensing surface areas but also necessary wettability in aqueous analytes. In this study, inexpensive, highly hydrophilic (contact angle < 5°), conducting (sheet resistance of 17 Ω □−1) porous fluorine-doped tin oxide (FTO) glass is fabricated from commercial FTO glass with a novel, simple, one-step Sn4+-based anodic treatment process, and used as a host electrode for electrochemical biosensors. We demonstrate its superior performance with hydrogen peroxide sensing. The hydrogen peroxide sensor is fabricated by simply depositing Pt nanoparticles onto the surface of the porous FTO substrate (PFTO) with a polyol process. Pt-decorated commercial FTO (CFTO) is also investigated as a control. The sensitivity achieved with the Pt-decorated PFTO is almost one order of magnitude higher than that of the Pt-decorated CFTO (25.8 vs. 2.69 mA M−1), and the response time is shortened from 36 s for the Pt-decorated CFTO to 1 s for the Pt-decorated PFTO. The PFTO proves to be a promising electrode substrate for host functional materials in electrochemical biosensors and can be readily applied to sensing of a wide variety of biosubstances.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...