Fluorescent and thermoresponsive supramolecular systems: synthesis, self-assembly and application in percutaneous optical monitoring†
Abstract
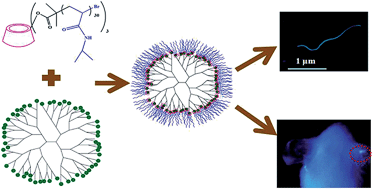
Supramolecular systems were constructed by the non-covalent coupling between PAMAM dendrimers with adamantyl groups and β-cyclodextrin graft PNIPAAm through host–guest interactions. Such supramolecular systems can further self-assemble into nanorods, which have thermoresponsive and excellent fluorescence properties. The injectable and percutaneous detection of fluorescent supramolecular systems will be of significant advantage in the future of biomedical monitoring.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...