Compatibility balanced antibacterial modification based on vapor-deposited parylene coatings for biomaterials†
Abstract
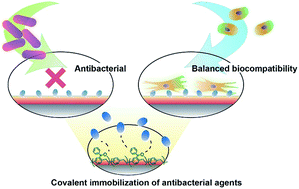
Advanced antibacterial surfaces are designed based on covalently attached antibacterial agents, avoiding potential side effects associated with overdosed or eluted agents. The technique is widely applicable regardless of the underlying substrate material. In addition, antibacterial surfaces are effective against the early stages of bacterial adhesion and can significantly reduce the formation of biofilm, without compromising biocompatibility. Here, this concept was realized by employing a benzoyl-functionalized parylene coating. The antibacterial agent chlorhexidine was used as a proof of concept. Chlorhexidine was immobilized by reaction with photoactivated benzoyl-functionalized surfaces, including titanium alloy, stainless steel, polyether ether ketone, polymethyl methacrylate, and polystyrene. A low concentration of chlorhexidine (1.4 ± 0.08 nmol cm−2) covalently bound to surfaces rendered them sufficiently resistant to an Enterobacter cloacae inoculum and its adherent biofilm. Compared to unmodified surfaces, up to a 30-fold reduction in bacterial attachment was achieved with this coating technology. The immobilization of chlorhexidine was verified with infrared reflection absorption spectroscopy (IRRAS) and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), and a leaching test was performed to confirm that the chlorhexidine molecules were not dislodged. Cell compatibility was examined by culturing fibroblasts and osteoblasts on the modified surfaces, revealing greater than 93% cell viability. This coating technology may be broadly applicable for a wide range of other antibacterial agents and allow the design of new biomaterials.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...