Novel methotrexate prodrug-targeted drug delivery system based on PEG–lipid–PLA hybrid nanoparticles for enhanced anticancer efficacy and reduced toxicity of mitomycin C†
Abstract
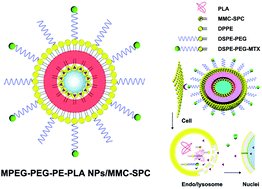
In the present study we have investigated novel MTX prodrug-targeted and MMC-loaded PLA–lipid–PEG hybrid NPs. These employ a double emulsion solvent evaporation method for the introduction of an anticancer drugs moiety of the MMC–soybean phosphatidylcholine complex or DSPE–PEG–MTX, in which the MTX prodrug can be exploited as a targeting ligand. The prepared drug delivery systems present a spherical shape, a small particle size (219.6 ± 2.1 nm) with narrow particle size distribution, high MMC encapsulation efficiency (90.5 ± 3.0%) and a sustained and pH-controlled MMC release. The advantage of the new drug delivery systems is that the two-anticancer drug moiety can coordinate the early-phase targeting effect with the later-phase anticancer effect. In vivo pharmacokinetics, following intravenous administration of the drug delivery systems, indicates a prolonged systemic circulation time of MMC. More importantly, the drug delivery systems exhibited a significant accumulation of MMC in the nuclei as the site of MMC action, which was indicative of the enhancement of anticancer activity. Such a design of drug delivery systems may open up a new horizon for targeted delivery and sustained and controlled release of MMC.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...