Surface functionalized barium sulfate nanoparticles: controlled in situ synthesis and application in bone cement†
Abstract
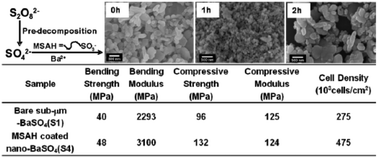
The controlled synthesis of surface functionalized BaSO4 nanoparticles with a diameter below 50 nm is achieved by combining the in situ generation of SO42− and the use of a difunctional surface modification agent, (2-(methacryloyloxy)ethyldimethyl-(3-sulfopropyl)ammoniumhydroxide (MSAH). Particularly, a pre-decomposition process of the SO42− precursor (S2O82−) is applied to decouple the in situ generation of SO42− and precipitation of BaSO4. As a result, the nucleation and growth of the BaSO4 particles is manipulated, which significantly reduces the particle size. Different combinations of the pre-decomposition time and MSAH/BaCl2 molar ratios showed a remarkable influence on the morphology and surface functionality of the BaSO4 particles. Furthermore, the morphology control by using other difunctional surface modification agents e.g. 3-sulfopropylmethacrylate potassium salt (SMPS) and 2-acrylamido-2-methylpropane sulfonic acid (AMSA) is examined. The MSAH-functionalized BaSO4 nanoparticles, used as s filler in bone cements, effectively improved the bending modulus and compressive strength of the poly (methyl methacrylate), PMMA, bone cements. The bone cement with MSAH-functionalized BaSO4 nanoparticles exhibited good radiopacity. Moreover, in vitro cell culture experiments demonstrated an improved biocompatibility compared to the bare BaSO4 particles. The MSAH-functionalized BaSO4 nanoparticles may be an ideal candidate material as a bone cement filler.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...