Gellan gum microgel-reinforced cell-laden gelatin hydrogels
Abstract
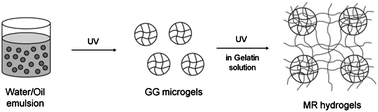
The relatively weak mechanical properties of hydrogels remain a major drawback for their application as load-bearing tissue scaffolds. Previously, we developed cell-laden double-network (DN) hydrogels that were composed of photocrosslinkable gellan gum (GG) and gelatin. Further research into the materials as tissue scaffolds determined that the strength of the DN hydrogels decreased when they were prepared at cell-compatible conditions, and the encapsulated cells in the DN hydrogels did not function as well as they did in gelatin hydrogels. In this work, we developed microgel-reinforced (MR) hydrogels from the same two polymers, which have better mechanical strength and biological properties in comparison to the DN hydrogels. The MR hydrogels were prepared by incorporating stiff GG microgels into soft and ductile gelatin hydrogels. The MR hydrogels prepared at cell-compatible conditions exhibited higher strength than the DN hydrogels and the gelatin hydrogels, the highest strength being 2.8 times that of the gelatin hydrogels. MC3T3-E1 preosteoblasts encapsulated in MR hydrogels exhibited as high metabolic activity as in gelatin hydrogels, which is significantly higher than that in the DN hydrogels. The measurement of alkaline phosphatase (ALP) activity and the amount of mineralization showed that osteogenic behavior of MC3T3-E1 cells was as much facilitated in the MR hydrogels as in the gelatin hydrogels, while it was not as much facilitated in the DN hydrogels. These results suggest that the MR hydrogels could be a better alternative to the DN hydrogels and have great potential as load-bearing tissue scaffolds.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Emerging Investigators

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...