The gadonanotubes: structural origin of their high-performance MRI contrast agent behavior†
Abstract
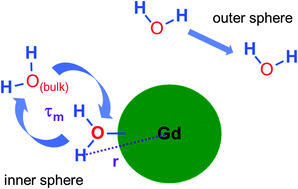
We present an X-ray absorption spectroscopy study of the local structure around the Gd3+ ions loaded within ultra-short carbon nanotubes (US-tubes). For this material, called gadonanotubes (GNTs), detailed modeling and analyses of the X-ray absorption near edge structure (XANES) and extended fine structure (EXAFS) data have helped decipher the structural origin of their exceedingly high-performance MRI contrast agent behavior. Analysis revealed that the Gd3+ ions are surrounded by ∼9 oxygen ions in the first coordination sphere with ∼3 O2− ions and ∼6 O2− ions, respectively, centered around 2.24 Å and 2.41 Å and that the Gd3+-ion sites in the GNTs are small. These sites are proton decorated once in solution through formation of the –(OH) and/or –(OH2) ligands. A large hydration number due to small Gd3+-ion sites and short Gd–O bonds, and thus short Gd–H distances, are the essential structural details pertinent to the high proton relaxivity observed for GNTs suspended in water.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...