Auto-adhesive transdermal drug delivery patches using beetle inspired micropillar structures†
Abstract
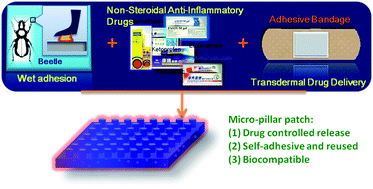
The patch described in this paper combines the principles of wet adhesion, which is a widely adopted biological adhesion system in nature, with transdermal drug delivery. A biologically inspired micropillar patch was fabricated that is self-adhesive, reusable, and can sustain a controlled drug release. We successfully preloaded the commercial non-steroidal anti-inflammatory generic drug unguents indomethacin, ketoprofen, diclofenac sodium and etofenamate into a polydimethylsiloxane elastomeric matrix and fabricated drug-containing micropillar patches. When examining the drug release kinetics and friction of the patches, we observed that these drug unguents can be released calculably and regularly for several days. Additionally, the drug unguents released from the patch to its attached surface are critical to increase the strength of the patch's adhesion, which is based on capillary attractive forces and is inspired by beetle feet. Here, we create a novel system combining biomimetics and drug delivery that can be modified for use across the biomedical and engineering spectra. Motivation: the objective of the present study was to characterize a micropillar PDMS patch that was inspired by a beetle's wet adhesion as a platform for conducting in vitro release studies. Commercially available non-steroid anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) were used as the model drugs for our delivery systems. An emphasis was put on quantitatively evaluating the drug release and friction manifestation of these patches.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...