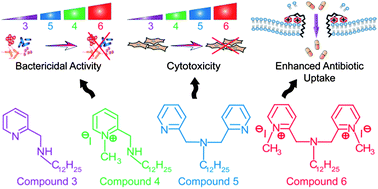
In this paper, we present a critical assessment of the therapeutic potential of low molecular weight pyridine-based synthetic amphiphiles based on structure-guided bactericidal activity and a rational evaluation of their cytotoxic potential. Fluorescence-based structure–function studies revealed that the amphiphiles were membrane-acting and displayed a hierarchical pattern of bactericidal activity, which could be correlated with their charge density and hydrophobicity. The membrane-targeting activity of the most potent cationic amphiphile (compound 6) was vindicated as it induced extensive membrane-disruption and dissipation of the transmembrane potential (ΔΨ) in pathogenic bacteria. At concentrations equivalent to the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) against the Gram-positive pathogen S. aureus MTCC 96, none of the amphiphiles exerted any cytotoxic effect on model human cell lines (HeLa, MCF-7 and HT-29). However, at elevated concentrations, a distinct gradation in the cytotoxic effect was manifested, which is probably accounted by the charge density and conformational flexibility of the amphiphiles. A viable therapeutic application of compound 6 is demonstrated in combinatorial assays, wherein the proclivity of the amphiphile to disrupt bacterial membranes at very low concentration is exploited to enhance the uptake and bactericidal efficacy of erythromycin against Gram-negative pathogenic bacteria.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...