Carbon nanotube decorated magnetic microspheres as an affinity matrix for biomolecules†
Abstract
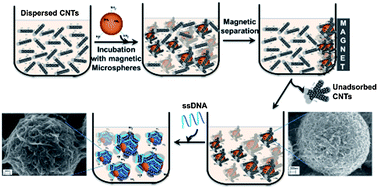
Carbon nanotube (CNT) decorated magnetic microspheres were fabricated to develop a multimodal platform that utilizes non-covalent molecular interactions of CNTs to magnetically separate biomolecules. Hybrid CNT-microspheres prepared by a feasible method reported herein had a well-defined structure as characterized by Raman spectroscopy and scanning electron microscopy. Binding interactions of resulting magnetic CNT-microspheres with DNA oligonucleotides were studied to demonstrate that single stranded DNA (ssDNA) in a solution can be effectively recovered by magnetic CNT-microspheres through strong physical wrapping of DNA around CNTs' walls. The magnetic character of these CNT-microspheres combined with their capability to bind other molecules including DNA allows their use as an affinity matrix that can be utilized in affinity separation of biomolecules, and also as a platform to monitor non-covalent binding interactions of CNTs with other biomolecules. As a proof of concept, we report on the use of these CNT-microspheres in in vitro selection of ssDNA aptamers against carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA), a cancer biomarker, by Systematic Evolution of Ligands by Exponential Enrichment (SELEX). ssDNA aptamer candidates that have strong affinity towards CEA were successfully separated magnetically from a pool of ssDNA (∼1014 molecules). Our results demonstrate that CNT-microspheres can serve as strong tools for affinity separation methodologies and can be utilized for various affinity pairs in solution.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...