Artificial magnetotactic probiotics for in vivo targeting therapy†
Abstract
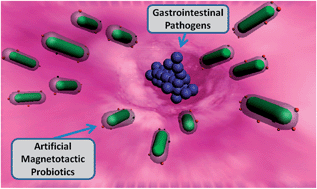
Artificial magnetotactic probiotics (AMPs) are developed to combine living probiotic benefits with magnetic targeting properties. Experimental investigations are carried out to study their surface nano-modification process, viability and magnetic motility behavior. Subsequent in vivo studies indicate that AMPs can be applied to inhibit different invasive pathogens, including some

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...