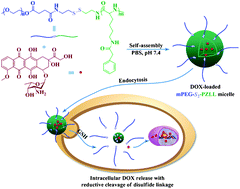
To develop biocompatible reduction-responsive micellar systems for efficient intracellular drug delivery, disulfide-linked block copolymers of methoxyl poly(ethylene glycol) (mPEG) and poly(ε-benzyloxycarbonyl-L-lysine) (PZLL) were synthesized through ring-opening polymerization of ε-benzyloxycarbonyl-L-lysine N-carboxyanhydride with amino group terminated disulfide functionalized mPEG as macroinitiator. The copolymers self-assembled into micelles in phosphate buffered saline (PBS) at pH 7.4 through direct dissolution and dialysis methods. The micelles were revealed to have excellent hemocompatibilities, and cell and tissue compatibilities, which rendered them with potential for drug delivery applications. Doxorubicin (DOX), an anthracycline antitumor drug, was loaded into the micelles through nanoprecipitation with a drug loading efficiency of about 30 wt%. The in vitro DOX release from all DOX-loaded micelles was accelerated in PBS with 10.0 mM GSH, mimicking intracellular reductive conditions. DOX-loaded micelles showed higher cellular proliferation inhibition towards glutathione monoester pretreated HeLa (a human cervical cell line) and HepG2 cells (a human hepatoma cell line) as compared to unpretreated or buthionine sulfoximine pretreated cells. The above results indicated that the biocompatible reduction-responsive micelles have vast potential in targeted intracellular delivery of antitumor drugs to achieve enhanced efficacy in malignancy therapy.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...