Electrochemical transformation reaction of Cu–MnO in aqueous rechargeable zinc-ion batteries for high performance and long cycle life†
Abstract
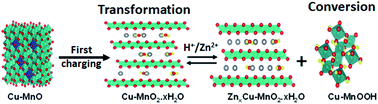
Rechargeable aqueous zinc-ion batteries (ZIBs) are emerging as an alternative to lithium-ion batteries in large-scale energy storage applications due to their safety and environmental friendliness. However, their application is hindered by the lack of suitable cathode materials that provide high capacity and long cycling stability. In this work, we have designed Cu–MnO nanospheres with abundant manganese/oxygen defects as a cathode material via calcination and reduction of manganese dioxide (MnO2) in an Ar/H2 atmosphere. Investigation of the electrochemical mechanism showed that the spinel-type Cu–MnO electrode started to transform into layered-type Cu–MnO2·nH2O nanoflowers upon initial charging, and thus, the subsequent Zn2+ intercalation and H+ conversion reactions took place in the Cu–MnO2·nH2O material. The underlying phase transformation of the Cu–MnO nanospheres and energy storage mechanism of the Cu–MnO2·nH2O nanoflowers were systematically investigated using a broad range of characterization techniques. Manganese vacancy was also observed in Cu–MnO2·nH2O, which interestingly triggered the lattice oxygen redox reaction. As a result, when employed as a cathode material in zinc-ion batteries, Cu–MnO2·nH2O delivered a high specific capacity of 320 mA h g−1 and long-term cycling stability with a capacity retention of over 70% after 1000 cycles. This work not only provides insight into the design of transition-metal-modified manganese monoxide cathodes but also broadens the horizon for understanding the electrochemical properties and energy-storage mechanism of low-valance manganese-based cathode materials in rechargeable zinc-ion batteries.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...