Holey graphene: an emerging versatile material
Abstract
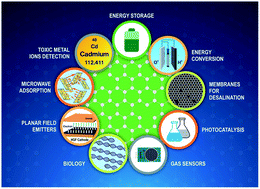
Holey graphene, also known as perforated graphene is formed by generating in-plane holes in basal planes of graphene based materials. By exploiting the combined advantages of holes and graphene, holey graphene based materials have attracted significant interest due to their exceptional properties such as high electrical conductivity and high surface area. These remarkable properties have enabled holey graphene based materials to outperform its pristine form (graphene) and demonstrate their applicability in versatile fields including electrical energy storage (supercapacitors and Li-ion, Li–air, Li–S and Na-ion batteries), energy conversion (electro-water splitting and dye-sensitized solar cells), water desalination, bioseparation, fuel cells, gas sensors, and hydrogen storage and dye degradation systems. As a consequence, it is important to uncover the prime properties and the related potential industrial implications of holey graphene based materials for the development of further research. Hence, in the review, the properties of emerging holey graphene-based materials and various applications including principles, design, fabrication, and engineering aspects are discussed in detail. The recent advances in the state-of-the-art hole generation methods for graphene-based materials along with their working mechanisms, associated issues/solutions, and possible future are discussed. Additionally, the review is aimed at providing critical views on the current status and prospects and generating novel ideas for the development of holey graphene-based materials as a formidable candidate for versatile applications.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Journal of Materials Chemistry A Recent Review Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...