Atomically dispersed metal dimer species with selective catalytic activity for nitrogen electrochemical reduction†
Abstract
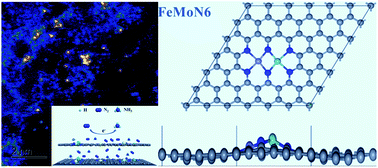
The electrocatalytic nitrogen reduction reaction (NRR) is emerging as an attractive strategy for sustainable and distributed production of ammonia (NH3) under ambient conditions. Because of the use of unsatisfactory electrocatalysts, however, it is still encountering issues of low yield rates and limited efficiency, resulting from the sluggish reaction kinetics, the competing hydrogen evolution reaction and additional reaction product formation. Herein, an atomically dispersed transition metal dimer species was employed to selectively accelerate the nitrogen reduction reaction kinetics for high reduction efficiency and simultaneously alleviate the additional reaction. In this system, atomic Fe and Mo metal dimer in situ anchored on defect-rich graphene layers can realize selective electroreduction of nitrogen to ammonia by numerous FeMoNxC active sites. It exhibits higher catalytic activity than its counterparts (Fe@NG and Mo@NG) owing to a combination of ligand, geometric and synergistic effects, with a yield rate of 14.95 μg h−1 mg−1 at −0.4 V and a faradaic efficiency of 41.7% at −0.2 V. The superior performance of this atomic transition metal dimer catalyst can outperform some precious metal-based catalysts due to its excellent selectivity and high catalytic activity. The specific structure of the N-coordinated FeMo dimer was further identified to be FeMoN6 by density functional theory (DFT). The catalytic reaction pathway and mechanism were explored by (DFT) calculations and proposed based on the FeMoN6 model. The existence of numerous FeMoN6 active sites can not only weaken the N![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) N bond, but also efficiently catalyze nitrogen reduction through the alternating pathway.
N bond, but also efficiently catalyze nitrogen reduction through the alternating pathway.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...