ZnO nanoconfined 3D porous carbon composite microspheres to stabilize lithium nucleation/growth for high-performance lithium metal anodes†
Abstract
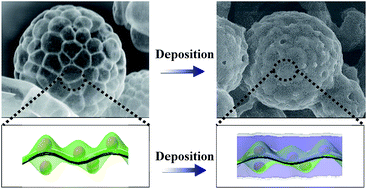
Lithium metal anodes have attracted considerable attention due to their high specific capacity (3860 mA h g−1). However, the volume change and the lithium dendritic growth of Li metal anodes impede their practical application. Researchers have improved the performance of lithium metal anodes by loading lithiophilic materials on 3D current collectors as lithium hosts. Nevertheless, the lithiophilic materials without spatial confinement may undergo severe volume and location changes during the cycling, leading to inhomogeneous lithium deposition, decayed structural stability and electrochemical performance. Herein, lithiophilic ZnO nanoparticle confined 3D porous carbon composite microspheres (3D ZnO@PCCMs) as hosts for lithium metal anodes were developed through a facile and scalable in situ strategy to mitigate the above formidable problems. The microsphere consists of several tens of interconnected empty carbon nanoboxes with ultra-small ZnO nanocrystals embedded in-plane. In the constructed architecture, the ZnO nanoparticles confined within ultrathin carbon walls can effectively prevent the ZnO from agglomerating and detaching from the current collectors during the cycling, inducing the uniform distribution and structural stability of ZnO for guiding the long-term homogenous lithium deposition, while the abundant interconnected empty boxes can sustain massive lithium deposition and accommodate the volume expansion of lithium during cycling. As a result, the as-obtained electrode with ZnO@PCCMs as a 3D host can achieve a very high coulombic efficiency, durability and stability even at high current density and areal capacity. This work delivers a novel concept that stabilizing the lithiophilic seeds can lead to a more stable and excellent cycling performance for lithium metal anodes, and meanwhile provides a low-cost and industrialized manufacturing approach for high-safety and high-performance lithium metal anodes.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...