Metal-ion-imprinted thermo-responsive materials obtained from bacterial cellulose: synthesis, characterization, and adsorption evaluation†
Abstract
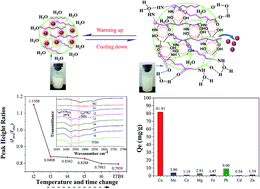
In this study, a novel gradient heating procedure was developed to fabricate the targeted metal-ion-imprinted thermo-responsive material, i.e. ion-imprinted thermo-responsive BC derivative (ITB), from bacterial cellulose using Cu2+ as a template and N-isopropylacrylamide (NIPAM) as a monomer; moreover, the structure and properties of ITB were analysed via various analytical techniques including FTIR spectroscopy, DSC, SEM, and Raman spectroscopy. The lower critical solution temperature (LCST) of ITB was 38.57 °C in the heating procedure, whereas it was 30.81 °C in the cooling procedure. The adsorption capacity of ITB for Cu2+ reached 95.20 mg g−1 at 45 °C (>LCST), the desorption rate was 98.81%, and desorption could be simply achieved by washing the adsorbents with water at 20 °C (<LCST). After repeating the adsorption–desorption procedure for 5 times, the adsorption capacity and desorption rate only slightly decreased to 91 mg g−1 and 97%, respectively. The adsorption kinetics was shown to follow the pseudo-second-order equation, whereas the adsorption isotherm was better fitted with the Langmuir equation. The maximum theoretical adsorption capacity for Cu2+ was achieved to be 140.85 mg g−1. In a mixture containing other metal ions (Mn2+, Ca2+, Mg2+, Fe3+, Pb2+, Cd2+, Zn2+, and Cu2+), the adsorption capacity for Cu2+ was 81.91 mg g−1, whereas that for other ions was between 0.54 and 9 mg g−1. The results indicate that ITB exhibits significant potential for selective separation and enrichment of metal ions by templating with Cu2+ ions as a model example.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2019 Journal of Materials Chemistry A HOT Papers


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...