Tuning the electrochemical behavior of organodisulfides in rechargeable lithium batteries using N-containing heterocycles†
Abstract
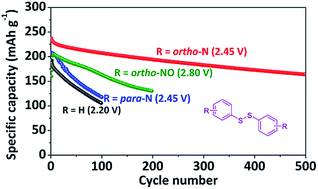
S–S bonds in organodisulfides can break and obtain Li+ and e− in the discharge of lithium batteries. Organodisulfides provide precise lithiation sites, and therefore are valuable models for the study of redox reactions in lithium batteries. To understand their electrochemical behavior, we investigate three disulfides with different N-containing heterocycles including 2,2′-dipyridyl disulfide (2,2′-DpyDS), 4,4′-dipyridyl disulfide (4,4′-DpyDS), and 2,2′-dipyridyl disulfide-N,N′-dioxide (DpyDSDO). The three disulfides all show higher discharge voltage plateaus due to the electron-withdrawing groups: DPDS (2.20 V) < 2,2′-DpyDS (2.45 V) = 4,4′-DpyDS (2.45 V) < DpyDSDO (2.80 V). In particular, 2,2′-DpyDS exhibits an outstanding 69% capacity retention over 500 cycles. Our theoretical simulations show that lithium pyridine-2-thiolate, the discharge product of 2,2′-DpyDS, forms compact clusters via N⋯Li⋯S bridges coordinated by lithium ions, which can help reduce its dissolution in liquid electrolyte, and therefore increase the cycle life. Liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry is demonstrated to be a powerful tool for the investigation of discharge/recharge products of soluble organodisulfides in rechargeable lithium batteries.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2019 Journal of Materials Chemistry A HOT Papers


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...