ZnO nanoarray-modified nickel foam as a lithiophilic skeleton to regulate lithium deposition for lithium-metal batteries†
Abstract
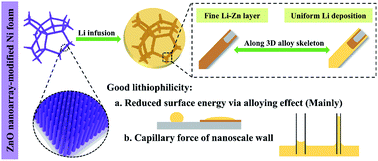
The search for high-energy-density rechargeable batteries has expedited the resurgence of metallic lithium (Li) as an anode in the energy storage field. Unfortunately, the practical application of Li-metal anodes is hampered because of intrinsic Li dendrite growth and volume change during cycling, which inevitably causes the fading of the battery lifespan and safety concerns. Here, tightly arranged ZnO nanorods were designed to enhance the lithiophilicity of a pristine Ni foam (NF). In this way, a homogeneous Li–Zn alloy layer could form spontaneously during the Li infusion process. This as-formed interlayer attached to the 3D conductive NF not only significantly ameliorated its affinity with molten Li, but also endowed it with fast kinetics for uniform Li nucleation. Thus, the greatly reduced nucleation barrier induced metallic Li to evenly strip/plate along a lithiophilic skeleton instead of bulk Li, minimizing the probability of dendrite formation and volume expansion. As a result, the ZnO nanoarray-modified nickel foam (ZMNF) delivered enhanced coulombic efficiency for the Li plating/stripping process along with a negligible nucleation overpotential. The symmetric cell obtained using the Li@LZMNF anodes could operate stably over 1200 h at 1 mA cm−2 and even over 300 h under 5 mA cm−2 with a fixed capacity of 2 mA h cm−2. The as-assembled full cells coupled with LiFePO4 and Li[Ni0.5Co0.2Mn0.3]O2 cathodes also exhibited excellent cycling stability and rate capability.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...