Self-supported ultrathin bismuth nanosheets acquired by in situ topotactic transformation of BiOCl as a high performance aqueous anode material†
Abstract
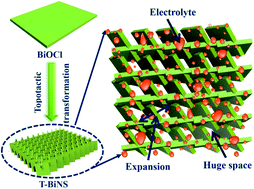
Aqueous rechargeable batteries are attractive because of their low cost, high operational safety and environmental benignity. Bismuth (Bi) with a highly reversible redox reaction and suitable negative working window has been investigated as a promising anode material recently. However, reported Bi anodes are still far from satisfactory because of their limited capacity and poor stability. Herein, self-supported ultrathin Bi nanosheets have been acquired by a very simple strategy of in situ topotactic transformation using BiOCl as the primary template (named T-BiNS). According to theoretical calculation, the space that T-BiNS has left after the release of O and Cl atoms is sufficient for the reversible charge/discharge process of Bi ↔ Bi2O3. The huge space and the unique structure enhance rapid electron transfer, reduce the activation energy and improve the stability. As such, T-BiNS shows a high capacity of 366 mA h g−1 (almost reaching a theoretical capacity of 384.7 mA h g−1) and good stability with a capacity retention of 82% after 5000 cycles. Finally, a NiCo2O4//T-BiNS full battery is fabricated, which exhibits a high energy density of 116 W h kg−1.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...