HxMoO3−y nanobelts: an excellent alternative to carbon electrodes for high performance mesoscopic perovskite solar cells†
Abstract
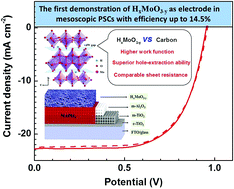
Carbon-based hole-conductor-free perovskite solar cells (C-PSCs) are considered as a promising photovoltaic technology toward commercialization, owing to their low cost and superior stability. However, efforts to further improve their efficiency have been hampered by the hole-extraction barrier at the Schottky contact between carbon and the perovskite. A conventional approach to resolve this issue is incorporating a hole-transport material (HTM) into the mesoscopic skeleton or chemical modification of the carbon electrode. Here, we show an innovative strategy that uses solution-processed hydrogen molybdenum bronze (HxMoO3−y) nanobelts, an n-type HTM with high work function and electrical conductivity, as the sole electrode material to enhance the hole-extraction process and realize efficient PSCs for the first time. The mesoscopic cell configuration of FTO/c-TiO2/m-TiO2/m-Al2O3/HxMoO3−y with perovskite infiltration delivered a champion power conversion efficiency (PCE) of 14.5%, which compares favorably with 13.3% of typical high temperature C-PSCs. This increase in cell efficiency stems primarily from the enhancement in open circuit voltage and short circuit current, which is due to the HxMoO3−y electrode with more favorable energy alignment and higher hole-extraction ability than the carbon electrode. These results show the potential of HxMoO3−y nanobelts as an efficient electrode for realizing high-performance mesoscopic PSCs.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2019 Journal of Materials Chemistry A HOT Papers


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...