Fabrication of regenerated cellulose nanoparticles by mechanical disintegration of cellulose after dissolution and regeneration from a deep eutectic solvent†
Abstract
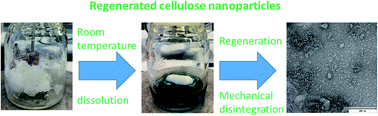
Cellulose nanoparticles are promising sustainable nanosized materials for use, for example, as nanofillers (such as reinforcement agents), green water purification chemicals, and oil dispersants. In this work, regenerated cellulose nanoparticles (RCNPs) were produced by mechanical disintegration of wood cellulose fibers and microcrystalline cellulose after dissolution and regeneration from a deep eutectic solvent (DES). An easily obtained DES based on guanidine hydrochloride and anhydrous phosphoric acid (molar ratio 1 : 2) was used to dissolve cellulose at room temperature. The degree of polymerization (DP) of cellulose was observed to decrease during the dissolution, whereas the crystallinity changed from cellulose I to cellulose II. After precipitation and washing, the regenerated cellulose was easily disintegrated to evenly distributed nanosized (diameter around 6 nm) fibrous cellulose nanoparticles. RCNPs were investigated as fillers in poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVA) composite films. Due to their small, fibrous and flexible nature, at low concentrations (1–5 wt%) RCNPs improved the elongation of the PVA film without diminishing its strength properties. At higher concentrations, RCNPs from wood pulp improved the tensile strength, as well as the modulus of PVA, similar to commercial cellulose nanocrystals. Therefore, this method provides a feasible way to obtain a unique nanosized cellulose material with good uniform size distribution and adjustable reinforcement properties.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...