Highly efficient adsorptive removal of uranyl ions by a novel graphene oxide reduced by adenosine 5′-monophosphate (RGO-AMP)
Abstract
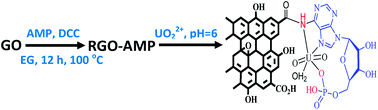
Graphene oxide reduced by adenosine 5′-monophosphate (RGO-AMP) has been developed as a smart nanoscale adsorbent for unprecedented high removal of uranyl ions from aqueous medium. The amine/amide and phosphate groups of AMP are grafted in the graphene oxide structure by reducing the carboxylic acid groups of GO to facilitate a stronger affinity for interaction with uranyl ions. An array of characterization techniques, e.g., Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, Raman spectroscopy, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), zeta potential and BET surface area measurements confirmed the functionalization of graphene oxide by AMP. The uranyl ion adsorption on RGO-AMP was qualitatively revealed from 2D elemental mapping recorded by field emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM) coupled with energy dispersive X-ray analysis (EDX) and by XPS analysis. The quantitative estimation of uranyl ion adsorption on RGO-AMP was done by inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectroscopy (ICP-OES). The adsorption followed a pseudo second order kinetic model and Langmuir adsorption isotherm, which revealed an adsorption capacity (qmax) of 3024 mg g−1 corresponding to 93% removal of uranyl ions in 240 s at an optimized adsorbent dose of 5 mg per 100 mL adsorbate solution taken at pH 6. Such high uranyl ion adsorption is attributed to the chelation of uranyl ions with the phosphate oxygen and with the aromatic nitrogen of the purine residue of AMP. This method exhibited high uranyl ion selectivity in the presence of interfering cations, viz. Al3+, Cd2+, Co2+, Cu2+, Fe2+, Hg2+, Pb2+, Mn2+, Zn2+, and Ni2+. The uranyl ion adsorption was thermodynamically favourable, spontaneous and endothermic in nature, while the XPS studies highlighted a probable adsorption mechanism. The sustainability of RGO-AMP as an adsorbent has been demonstrated by showing the regeneration and re-usability of the adsorbent for 5 cycles.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...