Highly thermally conductive flame retardant epoxy nanocomposites with multifunctional ionic liquid flame retardant-functionalized boron nitride nanosheets†
Abstract
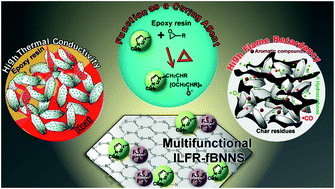
The low heat dissipation efficiency and serious security issues related to polymer-based thermal management materials (TMMs) have seriously limited their practical applications. However, simultaneously improving their thermal conductivity (TC) and flame retardancy is still a challenge due to performance limitations and complicated processing. Here, non-covalent ionic liquid flame retardant-functionalized boron nitride nanosheets (ILFR-fBNNSs) were used as a multifunctional nano-additive for fabricating epoxy (EP)-based nanocomposites with both superior TC and flame retardancy. Owing to its structural uniqueness and multifunctionality, the ILFR-fBNNS triggers resin crosslinking at a given temperature, while conferring significant improvements in dispersion and interfacial adhesion, thereby forming a thermally conductive network with reduced interfacial phonon scattering and a high-efficiency nano-barrier network acting synergistically with ILFR-induced char residues during thermal degradation. Therefore, the ILFR-fBNNS not only functions as a curing agent for fabricating the nanocomposites, but also acts as a thermal conductor and flame retardant for the nanocomposites. The optimal comprehensive performances of EP/ILFR-fBNNS nanocomposite are achieved with a 12.1 vol% ILFR-fBNNS content with TC enhancement of 478%, and reductions of up to 68.9% and 42.3% by microscale combustion calorimetry (42.4% and 37.7% by cone calorimeter) in peak heat release rate (PHRR) and total heat release (THR) respectively compared to neat EP.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...