Ti3C2 MXene as an excellent anode material for high-performance microbial fuel cells†
Abstract
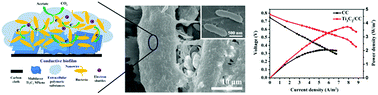
Microbial fuel cells (MFCs) as green and sustainable energy sources have attracted much scientific and technological attention in the past two decades. However, the low extracellular electron transfer (EET) and poor bacterial adhesion are still the major bottlenecks in the development of MFCs with high power output. In this work, a two-dimensional Ti3C2 MXene was used as the anode and successfully started up the MFC after 1 day of inoculation with a bacterial mixture, giving an output voltage of 640 ± 8 mV with an external resistance of 1000 Ω and a maximum power density of 3.74 W m−2, which was much higher compared to the carbon cloth (CC) control (550 ± 8 mV and 2.05 W m−2). The enhancement in the MFC output performance is attributed to the multilayer structure, high surface area and excellent conductivity of Ti3C2 MXene, which can provide enough nutrition for microbial growth and fast mass transfer, as well as more active sites for biological catalytic redox reactions. Moreover, the direct EET between the Ti3C2/CC anode and the microorganisms was facilitated by the outer membrane cytochromes, a highly dense network of microbial nanowires and high concentration of extracellular polymeric substances (shortening the gap between the microorganism and the solid surface), thus effectively improving the MFC performance. The Ti3C2/CC anode generated 23% of the coulombic efficiency, higher than that of CC (18.6%). Both of the anodes exhibited high chemical oxygen demand (COD) removal efficiency (94.6% for Ti3C2/CC and 94.0% for CC) based on sodium acetate media.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...