New insight into Na intercalation with Li substitution on alkali site and high performance of O3-type layered cathode material for sodium ion batteries†
Abstract
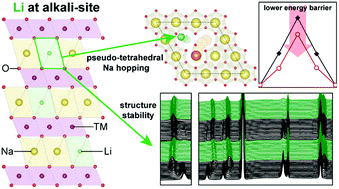
Lithium was substituted on the alkali site of an O3-type layered structure as cathode material for sodium-ion batteries (SIBs). Role of Li in Na intercalation and high performance is reported for the first time. The behavior of Na during intercalation is a critical factor that determines electrochemical performance. Although transition-metal oxides with layered structures have been studied extensively for SIBs, the focus has been on substitution at transition metal sites rather than at the alkali site. Here, substitution of Li at the alkali site of Nax[FeyMn1−y]O2 (0 ≤ x, y ≤ 1) layered materials is reported for the first time. The substituted element at the alkali site can directly interfere with the behavior of Na during intercalation. In situ XRD, synchrotron powder XRD, neutron powder diffraction, ex situ XANES, and DFT calculation revealed that Li at alkali sites stabilized the layered structure during the electrochemical reaction and assisted Na intercalation by lowering the energy barrier for Na-hopping. Contrary to common understanding, Li substituted material showed an improved cyclic and rate performance in spite of the smaller interlayer spacing of the O3-type layered structure. The result provides new insight into the role of a substituted element at the alkali site and shows that the Li at the alkali site is a key factor for achieving high performance of a layered cathode material.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...