An in situ eutectic remelting and oxide replacement reaction for superior thermoelectric performance of InSb†
Abstract
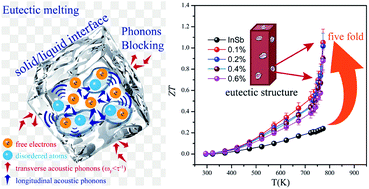
In this work, we demonstrate a synergistic approach to improve the thermoelectric performance of the InSb compound by introducing a replacement reaction of InSb and TiO2 during a hot pressing process. As a consequence of the replacement reaction, TiIn+ point defects, In2O3, stacking faults and InSb–Sb eutectic structures have been introduced into the InSb matrix. Accordingly, the electrical conductivity and the power factor (PF) have been significantly improved due to the electron donating nature of TiIn+ point defects, and the thermal conductivity has also been greatly reduced owing to the extra phonon scattering by dispersed In2O3 nanoparticles and stacking faults. More importantly, the melt of the introduced InSb–Sb eutectic structures plays an important role in filtering the transverse acoustic phonons, causing an abrupt reduction of lattice thermal conductivity at high temperature (753–773 K). Therefore, a relatively high ZT value ∼1.1 at 773 K has been obtained for the 0.1 wt% TiO2 added InSb sample. Moreover, the Vickers hardness of InSb also increases largely (∼210 Hv) deriving from the strengthening effects by introduced point defects and nanoinclusions, which is tougher than many well established mid-temperature TE materials.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...