Scalable synthesis of porous hollow CoSe2–MoSe2/carbon microspheres for highly efficient hydrogen evolution reaction in acidic and alkaline media†
Abstract
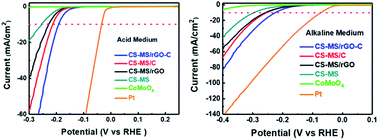
For the first time, porous microspheres of bimetallic CoSe2–MoSe2 hybrids with reduced graphene oxide and amorphous carbon (CS-MS/rGO-C) are synthesized through a facile, low-cost and scalable spray drying approach and a subsequent selenization process. The CS-MS/rGO-C electrocatalyst delivers excellent performance for the hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) in both acidic and alkaline media: in acidic solution, CS-MS/rGO-C has a very low onset potential of −142 mV vs. RHE and a low Tafel slope of 51.3 mV dec−1, and the overpotential at −10 mA cm−2 is as low as −195 mV vs. RHE; in alkaline media, the onset potential of CS-MS/rGO-C is −125 mV vs. RHE, and the Tafel slope is 83.2 mV dec−1, and the overpotential at −10 mA cm−2 is −215 mV vs. RHE. Moreover, it has outstanding long-term stability in both media even after 1000 cycles. The outstanding HER performance of CS-MS/rGO-C can be attributed to its bi-metallic composition, porous rGO-C microsphere structure, and conductive rGO-C skeleton, which can not only provide abundant active sites, but also guarantee high conductivity for CS-MS, thus facilitating the charge transfer. This work provides new insights into scalable synthesis of low-cost electrocatalysts with high efficiency and long-term stability, which can be extended to large-scale production of other advanced electrocatalysts to replace precious Pt-based catalysts for hydrogen evolution.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...