A study on the interfacial stability of the cathode/polycarbonate interface: implication of overcharge and transition metal redox†
Abstract
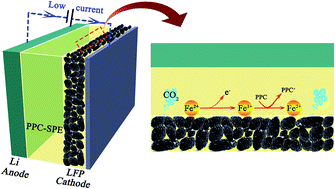
Polycarbonate electrolytes have attracted great interest in recent years due to their high ionic conductivity. However, the cathodic interfacial stability of polycarbonate electrolytes has yet to be explored. Herein, we reported an unusual reverse cation-redox reaction in which Fe3+ was reduced to Fe2+ by poly(propylene carbonate) (PPC) at the interface of a LiFePO4/PPC based solid polymer electrolyte during the first charge process at low current density. The XPS and in situ XRD results indicate the simultaneous existence of LiFePO4 (Fe2+) and FePO4 (Fe3+) in the overcharge process. Besides, the DEMS result indicates that CO2 could originate from the oxidation decomposition of PPC at the cathode surface. During this reaction, the oxidation of the polymer, rather than transition metal ions, serves as the source for charge compensation, leading to a significant overcharge issue. Furthermore, we found that the appearance of LiF on the cathode electrolyte interphase (CEI), tested by XPS, can stabilize the LFP/PPC interface. Consequently, a LiF layer is fabricated on the PPC-SPE surface, which significantly limits the overcharge issues.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...