An in operando study of chemical expansion and oxygen surface exchange rates in epitaxial GdBaCo2O5.5 electrodes in a solid-state electrochemical cell by time-resolved X-ray diffraction
Abstract
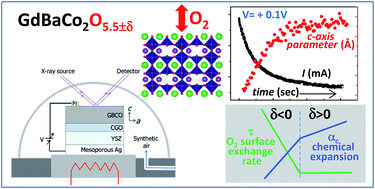
This report explores the fundamental characteristics of epitaxial thin films of a mixed ionic electronic conducting GdBaCo2O5.5±δ (GBCO) material with a layered perovskite structure, relevant for use as an active electrode for the oxygen reduction and evolution reactions in electrochemical devices. Time-resolved X-ray diffraction in combination with voltage step chrono-amperometric measurements in a solid state electrochemical cell provides a deeper insight into the chemical expansion mechanism in the GBCO electrode. The chemical expansion coefficient along the c-axis, αc, shows a negative value upon the compound oxidation contrary to standard perovskite materials with disordered oxygen vacancies. Chemical expansion also shows a remarkable asymmetry from αc = −0.037 to −0.014 at δ < 0 and δ > 0, respectively. This change in chemical expansion is an indication of a different mechanism of the structural changes associated with the variable Co cation oxidation state from Co2+ → Co3+ → Co4+. Since redox reactions are dominated by oxygen surface exchange between the GBCO electrode and gas atmosphere, monitoring the time response of the structural changes allows for direct determination of oxygen reduction and evolution reaction kinetics. The reaction kinetics are progressively slowed down upon reduction in the δ < 0 oxygen stoichiometry region, while they maintain a high catalytic activity in the δ > 0 region, in agreement with the structural changes and the electronic carrier delocalization when crossing δ = 0. This work validates the time-resolved XRD technique for fast and reversible measurements of electrode activity in a wide range of oxygen non-stoichiometry in a solid-state electrochemical cell operating under realistic working conditions.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...