Metal–organic framework derived nanoporous carbons with highly selective adsorption and separation of xenon†
Abstract
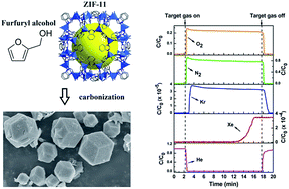
Xenon/krypton (Xe/Kr) separation is of industrial importance. Environmental concerns exist for pure noble-gas production and the reprocessing of noble-gas radioisotopes from used nuclear fuel. Cryogenic distillation as the main technology for Xe/Kr separation is energy and capital intensive. Thus, the development of a more economical and energy-efficient alternative, such as adsorptive separation based on solid porous materials, is urgent and significant. Herein, we prepared metal–organic-framework derived nanoporous carbons as new promising porous materials for highly selective Xe/Kr separation. A series of metal–organic-framework (MOF) derived nanoporous carbons (Z11CB-700, Z11CB-800, Z11CB-900, Z11CB-1000, Z11CB-1100, Z11CBF-1000-1, Z11CBF-1000-2 and Z11CBF-1000-3) were synthesized with ZIF-11 ([Zn(bIM)2], HbIM = benziminazole) as a precursor and furfuryl alcohol as an optional carbon source. A systematic investigation of the Xe/Kr separation was performed on these nanoporous carbons, and they were compared with commercial activated carbon. Z11CBF-1000-2 shows significantly high Xe Henry coefficient (80.01 mmol g−1 bar−1) and high thermodynamic Xe/Kr selectivity (19.7) at very low partial pressures relevant to nuclear-fuel reprocessing. Single-column breakthrough experiments indicate that the Z11CBF-1000-2 exhibits benchmark Xe capacity (20.6 mmol kg−1) under dynamic dilute conditions, which implies its promising potential to capture and separate Xe in used nuclear-fuel reprocessing facilities.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...