Screw-like PdPt nanowires as highly efficient electrocatalysts for methanol and ethylene glycol oxidation†
Abstract
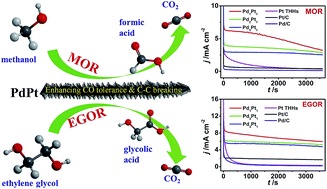
The performance of Pd and Pt based catalysts for electrocatalysis is closely correlated with their surface structures and compositions. In this paper we developed an electrochemical route to synthesize novel bimetallic screw-like PdPt nanowires (PdPt NWs) with tunable composition. The surface of the as-synthesized screw-like nanowires is extremely rough, bounded with high-index facets and thus exhibits a high density of active sites. The particular surface structure together with the synergetic effect and electronic effect accounts for the enhanced catalytic activity and durability towards methanol and ethylene glycol electrooxidation (MOR and EGOR). The activity of PdPt NWs is highly dependent on their composition; Pd1Pt1 NWs exhibit the highest catalytic activity for MOR that is 2.4-fold and 5.4-fold higher than that of the typical pure high-index Pt tetrahexahedrons (Pt THHs) and commercial Pt/C, respectively. It should be stressed that the initial activity of Pd1Pt1 NWs towards EGOR is close to that of Pt THHs but the stability of the Pd1Pt1 NWs can be significantly enhanced. In situ FTIR spectroscopic studies of the Pd1Pt1 NWs have revealed that their ability towards CO-tolerance is highly improved, and their capability of cleaving the C–C bond of EG is greatly promoted. This study has shed new light on the structure and composition tuning of PdPt nanocatalysts with high performance, which is of great significance for direct alcohol fuel cells.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...