Controlled synthesis of lithium doped tin dioxide nanoparticles by a polymeric precursor method and analysis of the resulting defect structure†
Abstract
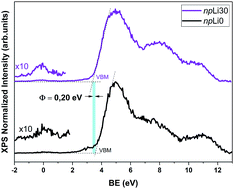
Recently, the high demand for the development of improved energy storage devices has brought the focus on tin oxide nanoparticles due to their ability to intercalate lithium. In order to strengthen the potential of the technological applications of Li doped SnO2, the synthesis of nanoparticles by a soft chemistry method with a highly homogeneous controlled size, high crystallinity and concentration of effectively incorporated Li over the range of 10 to 30 cat% is reported in this study. Li doped SnO2 nanoparticles were prepared with sizes between 4 nm (for undoped material) and 11 nm (for the 30 cat% Li doped nanoparticles). The samples were thoroughly characterized using different complementary techniques to determine the defect structure and electronic surface properties, whose knowledge is of the utmost relevance for achieving the desirable properties needed for implementation in different applications. The results indicate that lithium is incorporated mainly in substitutional sites in the rutile structure of tin oxide. On increasing the lithium content in the nanoparticles, the amount of oxygen vacancies reduced and a shift in the Fermi level, which was pinned at the surface defects, toward the maximum of the valence band was obtained. In the samples with the highest Li content, the local environment of lithium at the nanoparticle surface resembled the environment of Li in lithium oxide. Several intra-gap recombination defect levels were detected in the visible range, which are related to intrinsic tin oxide defects such as vacancies in different configurations. In addition, a defect level at 3.1 eV is also exhibited with increasing intensity in Li doped nanoparticles.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...