Advanced sodium storage property in an exfoliated MoO3 anode: the stability and performance improvement by in situ impedance mapping†
Abstract
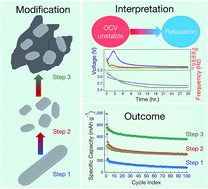
Inexpensive energy storage with impeded capacity fading is the goal for today's consumer market. An oxide-based sodium battery electrode is an inexpensive candidate, although it does not solve the fading issue. Here, the fading issue has been resolved by understanding the electrochemical stability followed by material modification. An exfoliated metal oxide (α-MoO3) maintaining good crystallinity, contouring a stable material phase, is investigated to ameliorate the storage properties. Herein, we describe an amenable technique, in situ impedance mapping, to discern the electrochemical stability just after cell fabrication. The result reflects an initial OCV instability which is depicted as a regular increase in Rct. Hence, sufficient rest (30 h) is imposed to reach a stable OCV, after which the anode is subjected to capture Na-ions. In conjunction with an inexpensive, additive-free organic electrolyte system, the modified anode material (rGO–MoO3) performs reversibly to store ∼0.75 A h mass specific (gm) capacity with adequate capacity retention until 100 cycles. We believe that the understanding and adoptable appraisal of impedance mapping will advance the next generation of energy storage systems.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...