Morphology stabilization strategies for small-molecule bulk heterojunction photovoltaics†
Abstract
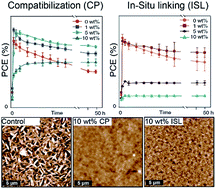
The greater crystallinity of solution-processed small-molecule organic semiconductors, compared to their polymer counterparts, renders the bulk heterojunction (BHJ) more susceptible to phase separation under thermal stress, decreasing device performance. Here we demonstrate and compare strategies to stabilize the donor:acceptor BHJ in DPP(TBFu)2:PC61BM solar cells using molecular additives designed to either afford compatiblization (CP) of the bulk heterojunction, or to in situ link (ISL) the components using a functional azide group. Both additives were found to stop phase segregation of the BHJ under thermal stress. At 5 wt% loading the ISL additive prevents phase segregation, while altering the azide reaction mechanism by using UV-induced linking versus thermal induced linking was found to significantly affect the device performance. Including 5 wt% of the CP additive slowed phase segregation and devices retained 80% of their optimum performance after 3000 min of thermal treatment at 110 °C (compared to 50% with the control). The CP additive at 10 wt% changed drastically the kinetics of phase segregation leading to devices with no decrease in performance over 3000 min thermal treatment. Thin film morphology characterization together with photoluminescence and impedance spectroscopy give further insight into the performance differences between the additives. These results reinforce the conclusion that the compatiblization method is the most promising strategy to engineer highly-efficient thermally-stable organic photovoltaics based on solution-processed small molecules.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...