Encapsulating a high content of iodine into an active graphene substrate as a cathode material for high-rate lithium–iodine batteries†
Abstract
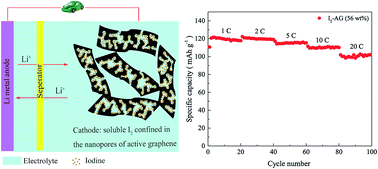
Rechargeable lithium–iodine (Li–I2) batteries are a promising electrochemical energy storage candidate due to their high energy and power density. However, the high solubility of iodine in electrolytes seriously deteriorates the electrochemical performance of Li–I2 batteries. In addition, the low iodine content in the cathode impedes the enhancement of energy density. Active graphene (AG) has a large specific surface area, abundant micropores and mesopores, free inter-particle voids and unimpeded ion diffusion channels, making it a promising substrate for loading a high content of iodine. In this study, I2–AG composites were fabricated through an in situ iodine deposition route. The facile synthesis process can introduce a high content of iodine into the nanopores of AG effectively. The microstructure and morphology of the I2–AG composites were characterized using Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET), X-ray diffraction (XRD), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) methods. The results show that iodine is well dispersed in the nanopores of AG. The as-prepared I2–AG composites exhibit high specific capacity, excellent cyclic performance and high rate performance. In particular, the I2–AG composite, with a high iodine content of 56 wt%, delivers a high capacity of 218 mA h g−1 at a 1C rate, and maintains 161 mA h g−1 after 500 cycles, corresponding to a low capacity fading of only 0.023% per cycle. Especially, the I2–AG composite exhibits outstanding high-rate performance. Even at 20C, an appreciable discharge capacity of 184 mA h g−1 can still be obtained. The results indicate that the high content of soluble iodine can be well constrained in the nanopores of AG during charging and discharging processes, making Li–I2 batteries a promising alternative energy storage device with both high energy and high power density.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...