Controllable synthesis of highly uniform flower-like hierarchical carbon nanospheres and their application in high performance lithium–sulfur batteries†
Abstract
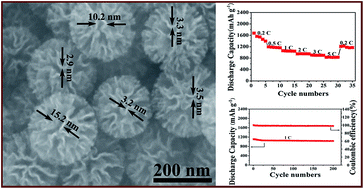
Elemental sulfur cathodes for lithium/sulfur batteries are receiving intense interest owing to their high theoretical capacity and energy density. However, they still suffer from severe capacity fading and moderate rate capability. Herein, we provide rational design and controllable fabrication of highly uniform flower-like hierarchical carbon nanospheres (FCNS) for sulfur accommodation for lithium/sulfur battery cathodes. The as-prepared three dimension FCNS with a size of around 200 nm seem to be assembled by petal-like carbon nanosheets with a thickness of about 4 nm, forming many mesoporous channels, which lead to their high surface area and large pore volume. With such a tailor-made structure, FCNS/sulfur composite cathodes with high sulfur-loading (81 wt%) deliver high specific capacity, long cycling life and excellent rate capability. Particularly, N-doped flower-like carbon nanospheres (NFCNS) with higher surface area (1223 m2 g−1) and larger pore volume (2.33 cm3 g−1) are also fabricated by treating with NH3 and used to host sulfur in lithium–sulfur battery cathodes, exhibiting more excellent rate capability (829 mA h g−1 at 5C) and cycling stability with a decay of 0.03% per cycle over 200 cycles at 1C. Even though the area density is improved to 2.5 mg sulfur per cm2, the battery still has a decay of 0.056% per cycle over 200 cycles.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...