Superhydrophobic self-floating carbon nanofiber coating for efficient gravity-directed oil/water separation†
Abstract
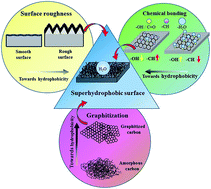
The fabrication of a superhydrophobic carbon nanofiber (CNF) on various substrates (activated carbon fiber and glass) via a two-step process (plasma sputtering followed by chemical vapor deposition at a lower operating temperature of 300 °C) is reported, eliminating the need for multiple pre- and post-treatments with toxic chemicals (fluorine/Si-based chemicals, metal salts, and organic solvents). Entangled CNFs grown on the coated activated carbon fiber (ACF) and glass substrates showed superhydrophobicity with water contact angles of 146° and 156°, respectively. The superhydrophobicity of the coated substrate is attributed to its lower surface energy, more graphitic structure (lower ID/IG ratio) as observed by Raman spectroscopy, lower carbonization state ratio (sp3/sp2 ratio) and restricted carbonyl (C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O) as analyzed by X-ray photo-electron spectroscopy, and hydroxyl functional groups (–OH) as shown by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. Coated substrates were found to be stable in both acidic and basic chemicals. The load carrying capacity of the deposited CNF was measured to be up to 153 times that of its own deposited weight. The coated ACF was used for oil/water separation and showed a separation efficiency of >99%. Thus, the as processed durable CNF coated substrates can potentially be used for many applications such as anti-wetting, corrosion resistance, support for floating aquatic micro-devices and oil–water separation applications.
O) as analyzed by X-ray photo-electron spectroscopy, and hydroxyl functional groups (–OH) as shown by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. Coated substrates were found to be stable in both acidic and basic chemicals. The load carrying capacity of the deposited CNF was measured to be up to 153 times that of its own deposited weight. The coated ACF was used for oil/water separation and showed a separation efficiency of >99%. Thus, the as processed durable CNF coated substrates can potentially be used for many applications such as anti-wetting, corrosion resistance, support for floating aquatic micro-devices and oil–water separation applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...