From ionic liquid-modified cellulose nanowhiskers to highly active metal-free nanostructured carbon catalysts for the hydrazine oxidation reaction†
Abstract
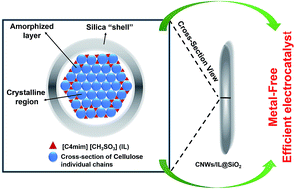
Ionic liquid (or [C4mim][CH3SO3])-modified cellulose nanowhiskers (CNWs) are synthesized and successfully used as precursors to make heteroatom (N and S)-doped nanostructured carbon catalysts. The catalysts can efficiently electrocatalyze the hydrazine oxidation reaction (HOR) with an onset potential close to the reaction's thermodynamic value, or with a value better than those obtained for other related materials. The synthesis of these metal-free carbon electrocatalysts generally involves only a few, relatively less demanding synthetic steps. Based on relevant control experiments, the outstanding catalytic activity of the materials is attributed to the heteroatom dopants and defect sites in the materials, which form during carbonization due to the [C4mim][CH3SO3] placed around the CNWs. However, it is not necessarily the density of heteroatom dopant species introduced into the nanostructured carbon materials by the ILs that directly affect the electrocatalytic activity of these materials; it is rather the specific type of dopant-associated chemical moiety and vacancy site created in the materials, which are the main factors positively affecting the electrocatalytic activity of the materials toward the reaction. The surface areas of the materials play a relatively lesser role in affecting the electrocatalytic properties of the materials toward the HOR as well.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...