Control of preferred orientation with slow crystallization for carbon-based mesoscopic perovskite solar cells attaining efficiency 15%†
Abstract
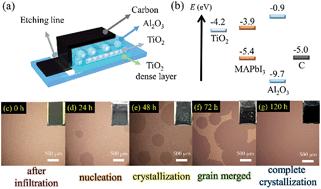
To produce mesoscopic carbon-electrode-based solar cells free of a hole-conduction layer, we developed a simple one-step drop-cast method (temperature 20 °C, relative humidity 50%) to grow uniform and compact perovskite nanocrystals via slow crystallization (SC). X-ray diffraction (XRD) results indicated that perovskite nanocrystals produced inside the mesoporous TiO2/Al2O3/C layers according to our SC approach with N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone (NMP) as a precursor solvent showed a preferred orientation at facet (004) with large crystalline grains, whereas those produced with other solvents or via thermal annealing (TA) methods showed greater intensity at facet (220) with small crystals. After the SC (NMP) procedure was completed, additional TA treatment would change the preferred orientation from (004) back to facet (220), which would break the connectivity and lose the uniformity of the crystals, causing the grains to become significantly smaller. Transient photoluminescence (PL) decay profiles of the SC devices made with four precursor solvents, NMP, γ-butyrolactone (GBL), dimethylformamide (DMF) and dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), were recorded to show the trend of charge separation kinetics of the perovskite crystals inside the mesoporous films, which is consistent with the trend of the corresponding device performance showing the same order. The SC (NMP) device attained the best efficiency of power conversion (PCE), 15.0%, with average value (13.9 ± 0.5%), which is much superior to those devices from either the traditional one-step TA (DMF) method (5.2 ± 1.0%) or the traditional sequential TA method (10.1 ± 0.7%). This work emphasizes the significance of the control of preferred orientation of perovskite nanocrystals using the SC approach, to obtain high-performance carbon-based mesoscopic solar cells with excellent reproducibility and stability.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...