Surface engineering of carbon fiber paper for efficient capacitive energy storage†
Abstract
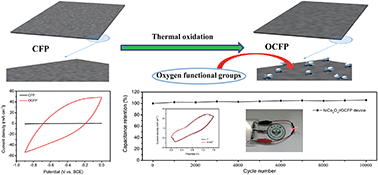
Commercial carbon fiber paper (CFP) has been rarely used as an active electrode material for supercapacitors (SCs) due to its poor electrochemical activity and limited surface area. Herein, we report a facile, scalable and effective thermal oxidation method to directly activate CFP as a robust electrode material in SCs. Significantly, the activated CFP electrode exhibits a high areal capacitance of 0.75 F cm−2 at 5 mA cm−2 and excellent rate capability as well as cycling performance. Moreover, an advanced asymmetric supercapacitor (ASC) device with a remarkable energy density of 2.3 mW h cm−3 and outstanding long-term durability is achieved based on the as-obtained activated CFP electrode as the anode.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...