Synthesis of nanoporous structured iron carbide/Fe–N–carbon composites for efficient oxygen reduction reaction in Zn–air batteries†
Abstract
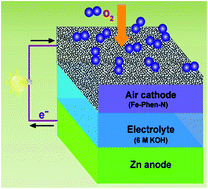
Large-scale industrial level applications of fuel cells and metal–air batteries have called for the development of highly efficient and low-cost oxygen reduction electrodes. Here we report the effective and simple preparation of iron carbide-embedded Fe–N-doped carbon (Fe3C/Fe–N/C) composites using an iron–phenanthroline (Fe–Phen) complex and dicyandiamide (DCA) as the precursors that are subsequently heat treated. The optimal catalyst pyrolyzed at 800 °C (Fe–Phen–N-800) exhibits superior oxygen reduction activity with onset and half-wave potentials of 0.99 and 0.86 V in 0.1 M KOH, respectively, which are higher than those of Pt/C (onset and half-wave potentials of 0.98 and 0.84 V) at the same catalyst loading. Moreover, the obtained Fe–Phen–N-800 displays comparable activity to Pt/C in 0.1 M HClO4 solution. Notably, the well-developed Fe–Phen–N-800 catalyst shows much higher long-term stability and better methanol tolerance than Pt/C. The results suggest that our catalyst is one of the most promising candidates to replace Pt catalysts toward oxygen reduction. Strikingly, a primary Zn–air battery using Fe–Phen–N-800 as the air cathode catalyst delivers higher voltages and gravimetric energy densities than those of a Pt/C-based system at the discharge current densities of 10 and 25 mA cm−2, thus demonstrating the potential applications of our catalyst for energy conversion devices.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...