Metal–semiconductor double shell hollow nanocubes for highly stable hydrogen generation photocatalysts†
Abstract
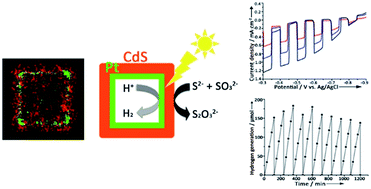
Noble metal–CdS double shell hollow nanocubes were synthesized by sequential four-step nanoscale reactions, including galvanic replacement, sulfidation, cationic exchange, and reduction. The photocatalytic H2 generation using these hollow nanocubes indicated significant competition between electron transfer and electron–hole recombination, and showed remarkable stability against photocorrosion.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...